What You Should Know About Treating Migraines With Botox

Botox is a popular noninvasive cosmetic procedure that effectively gets rid of facial wrinkles and fine lines. And during its early uses, women who received the Botox cosmetic treatment also noticed an improvement to their headache pain. Since then, Botox has been widely studied for treatment of chronic migraine headache until it finally gained its FDA approval in 2010.
So how exactly does Botox work for treating migraines? Much like how it is given for cosmetic purposes, Botox is injected to the head and neck muscle areas where it disrupts the pain transmission by inhibiting release of chemical and pain signal activity. It’s an effective preventive treatment for migraine headaches by stopping pain before it even starts.
With just a few simple injections, our providers can erase your wrinkles and fine lines in no time with Botox. Call us today to book your appointment.
What Causes Chronic Migraine Headaches?
Migraines and headaches are two different neurological disorders characterized by disabling throbbing pain. To know which treatment you need to get to manage the pain, it’s important to be able to identify the different symptoms and causes of a regular headache and chronic migraine:
1. Headache
Pain that is localized on one side of the head or pressure that is felt from one region to another is called a headache. The common areas for headache pain are the forehead, temples, and the back of the neck. This condition can be further classified into two specific types: primary headache and secondary headache.
A primary headache occurs due to oversensitivity or inflammation of the pain-sensitive parts of the head. This can include fluctuations in chemical activity in the brain or swelling of the nerves, blood vessels, and muscles surrounding the head or neck.
External factors such as poor lifestyle habits, not getting enough sleep, stress, anxiety, and too much eating of processed food can trigger headaches. The most common kinds of primary headaches are:
- Cluster headache – Severe headaches of the cluster type usually occur in one region of the head. A patient with cluster headache often experiences bursts of pain in periods or patterns.
- Tension headache – When a patient has tension type headache, they may feel pressure on the expanse of their forehead or the sides and extend to the back of the head.
- Chronic headache – A unique feature of chronic headaches is that they can last for more than 15 days per month.
Meanwhile, a secondary headache is often caused by underlying medical illnesses that have an effect on the nerves in the brain. Some of the medical conditions that can cause secondary headache pain are brain tumors, aneurysm, high blood pressure, stroke, head trauma, seizures, and sinus infections. Overuse of oral medication for migraine pain can also cause secondary headaches.
2. Chronic Migraine
A migraine headache is a chronic type of headache that is more intense in pain sensation and has accompanying symptoms of nausea, vomiting, mood changes, neck stiffness, and increased sensitivity to light, sounds, and smells.
Chronic migraine headaches are recurrent in nature and patients may have a headache frequency of 15 days and more each month. On the other hand, its counterpart, episodic migraine, is diagnosed by no more than 15 chronic headache day per month.
Triggers of a migraine attack are different per person but these may include hormone changes (for women), stress, exhaustion, dehydration, caffeine withdrawal, and certain food and drinks.
Migraine attacks usually come in phases: prodome, aura (characterized by visual and auditory disturbances), migraine phase (headaches can last up to 72 hours), and postdrome (lingering pain and exhaustion after an attack).
How Does Botox Treat Migraines?
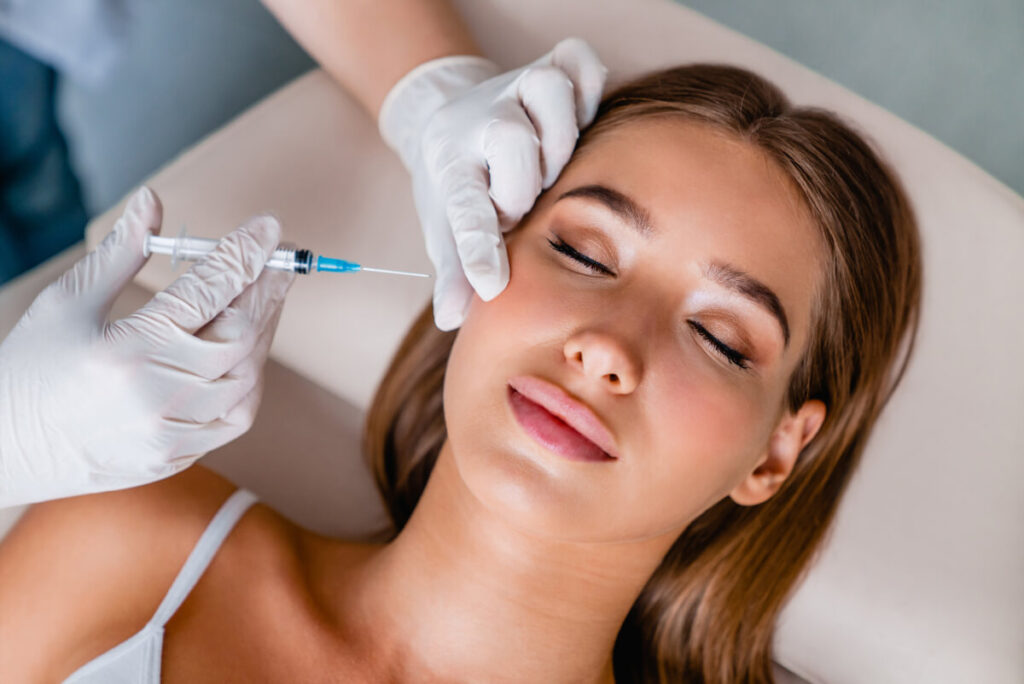
Acute medications are the common chronic migraine treatment and they offer temporary pain relief so you can return to your normal activities and function. But for those looking for long-term comfort from chronic migraine headache symptoms, Botox may be the solution for you.
Botox is a purified protein form of botulinum toxin, a neurotoxin that is extracted from the Clostridium botulinum bacteria. While cosmetic Botox injections is its most popular form, it is also beneficial for patients with strabismus, overactive bladder, cervical dystonia, muscle spasticity, excessive sweating, and chronic migraine.
The botulinum neurotoxin is a well-known neuromodulator and when used as a wrinkle treatment, it acts by blocking the pathways of chemicals that are responsible for muscle contraction and eventually smooths out the wrinkles and lines on the skin. Using Botox treatment for chronic migraine applies the same mechanism of action to help manage pain.
A botulinum toxin injection for chronic migraine has a direct effect on the pain fibers or the nerves that release stimuli which activate pain transmission. When Botox blocks these nerve endings, the pain signals are prevented from reaching the muscles which reduces the throbbing pain of migraine headaches.
Read more: The Pros and Cons of Botox for Migraines
How Often Do You Need Botox For Chronic Migraine?
To successfully prevent migraine from recurring, a migraine sufferer can get Botox injections for 4 times a year. An average total of 155 Botox units are needed for migraine treatment and they are given to 7 injection sites across the head and neck muscle areas which doctors recognize as the trigger points where pain usually starts to begin. The treatment can take 2 to 3 weeks to have full effects.
Also, it should be noted that Botox injection is only used for chronic migraine treatment and it may not be as effective for other types of headache. You should first discuss your migraine symptoms with your doctor or a headache specialist before deciding on getting Botox. It’s also recommended to keep a headache diary and track your symptoms to help identify what type of headache you have.
The Side Effects of Botox for Migraines
Botox treatments are generally safe and guarantee desirable results as long as they are performed by an experienced provider. Most side effects of Botox for migraines are mild and they are usually resolved within a few days. These can include:
- Pain and swelling at the injection site – They are easily remedied by an ice pack or cold compress over the treatment area.
- Neck pain – At least 9% of Botox for migraine patients may experience neck pain according to clinical studies.
- Minor headache
Serious complications are very rare and can only happen if the toxin has spread to other areas of the face and body. The possible adverse reactions are muscle weakness, droopy eyelid, dry mouth, trouble speaking or breathing, and shortness of breath.
Sign Up For Safe Botox Treatments at aNu Aesthetics
Botox is now an accepted migraine prevention treatment and can be considered for long-term therapy so that patients can do their work and enjoy activities without worries of chronic pain. When you choose to receive Botox, finding a trusted and skilled provider is necessary to ensure safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
aNu Aesthetics is a premier medical spa and wellness clinic that offers quality Botox treatments. We are committed to providing excellent patient care and service, and we design our cosmetic and wellness programs to cater specifically to your needs. Contact us now to learn more about our services or schedule a consultation with one of our doctors.
With just a few simple injections, our providers can erase your wrinkles and fine lines in no time with Botox. Call us today to book your appointment.